What is Tendinitis?
Tendinitis is inflammation or irritation of a tendon — the strong connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone.
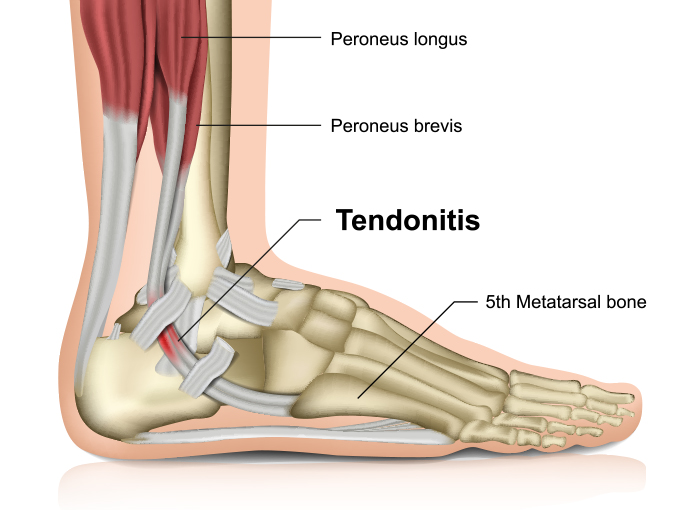
What is Tendinitis? Does ROC treat Tendinitis?
Tendinitis is inflammation or irritation of a tendon — the strong connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone. Tendinitis symptoms include pain, stiffness, and tenderness near a joint.
Providers at ROC are able to perform a thorough evaluation to determine the appropriate diagnosis and initial treatment for tendinitis.
What causes Tendinitis? Where does it occur?
Tendinitis is caused by inflammation in the tendons around joints that are exposed to repetitive activity, or excessive use. Overuse of the muscles connected to the tendons can cause inflammation that is persistent. Persistent inflammation can cause damage to the tendon if the condition is not appropriately treated.
Some common names for various tendinitis problems are:
- Outside of the forearm: “Tennis elbow”
- Inside of the forearm: “Golfer’s elbow”
- Upper arm: “Pitcher’s shoulder”
- Front of the lower leg and knee: “Jumper’s knee”
- Front of the lower leg: “Shin splints”
What are the symptoms of tendinitis?
Signs and symptoms of tendinitis tend to occur at the point where a tendon connects a muscle to a bone, typically near a joint. These include pain with moving the joint, arm or leg, tenderness with pressure, and swelling.
When should I see ROC for tendinitis?
If you suspect tendinitis, your ROC provider can make the diagnosis and initiate treatment. If the pain, swelling, and joint stiffness is severe and affecting normal activities, an evaluation at ROC is recommended.
What are the causes of tendinitis?
Repetitive motion and loading of a tendon are the most common causes of tendinitis. Tendinitis is uncommonly the result of an acute injury, but can flare up with sudden activities. Although tendinitis can be caused by a sudden injury, the condition is much more likely to stem from the repetition of a particular movement over time. Most people develop tendinitis because their jobs or hobbies involve repetitive motions, which put stress on the tendons.
Risk factors for developing tendinitis include age, improper conditioning, working in particular jobs, especially having to work for prolonged periods of time in a certain position, frequent exertion, vibration (for example, jack hammer operator) or certain sports.
What are the complications associated with tendinitis?
The two major complications associated with tendinitis are tendinosis, and tendon rupture. Tendinosis involves a weakening of the tendon due to chronic inflammation. It can lead to chronic pain, weakness, and is a risk factor for tendon rupture. Tendon rupture is associated with significant pain, disability, and swelling. Tendon ruptures frequently require surgery to avoid permanent disability.
How can tendinitis be prevented?
The primary means of preventing tendinitis is the avoidance of the activities associated with overuse of the affected body part. Proper techniques (work, exercise training) are highly recommended if the problem recurs following an episode of tendinitis. When tendinitis is associated with work activities, appropriate work ergonomics is advisable. Recreational athletes must take care to train properly for activities that have caused tendinitis and may consider alternative forms of exercise if the problem becomes persistent.
How can tendinitis be treated at ROC?
Providers at ROC will perform a thorough diagnostic evaluation to determine whether tendinitis is the source of your pain. The most important initial treatment for tendinitis is usually cessation of the offending activity (if possible), so that healing can occur. ROC providers can also make referrals for Physical therapy techniques that can be utilized to reduce pain and inflammation. Overt-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications and cortisone injections are also commonly used to reduce pain and inflammation to allow for proper healing.